产业研究
月
年
What are the drivers of enterprise diversification in Chinese cities: Coming from path-dependence or path-creation forces?
Most studies in evolutionary economic geography considered path-dependence forces that drove regional diversification in the macro level. This view generated debates recently and path-creation forces began to attract large concern. This study focuses on revealing the driving forces of Chinese enterprise diversification in the micro level. It first proposes invention patents as an indicator to measure internal path-creation force on double “spatial-industrial” dimensions based on China Economic…
月
年
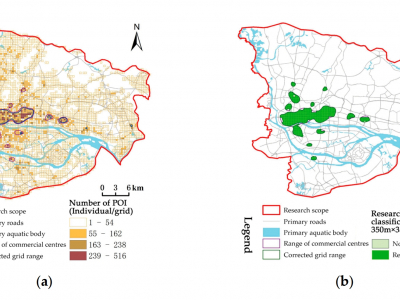
The Impact of Commercial-Industry Development of Urban Vitality: A Study on the Central Urban Area of Guangzhou Using Multisource Data
Urban commercial centers play a critical role in the development of cities, and it is of significant relevance to research the influencing variables of the urban vitality of commercial centers to improve the quality of urban commercial centers. This study employs big data to construct a multiple linear regression model in order to uncover the spatial-distribution characteristics of urban vitality and commercial sectors in commercial centers within the primary urban region of Guangzhou. The…
月
年
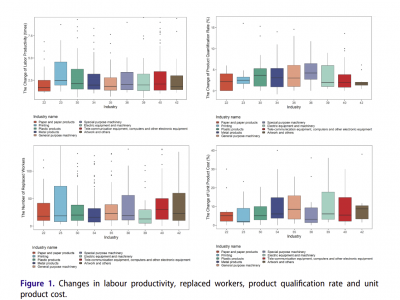
Automation, firm employment and skill upgrading: firm-level evidence from China
The present empirical study investigated the impacts of automation technology on employment at the firm level in Dongguan, China.Results of propensity score matching (PSM) and difference-indifference (DID) modelling show that automation technology increases the total employment as well as employment associated with workers at all skill levels of firms, indicating that the productivity effect is stronger than the displacement effect in manufacturing firms. Furthermore, automation technology has…
月
年
内生演化与外部联系:演化视角下珠江三角洲工业机器人产业的兴起
摘要:在当前新一轮技术变革的背景下,培育新兴产业对于转换区域发展动力、塑造区域竞争优势都有重要意义。文章以演化经济地理学为理论基础,构建了在制度环境作用下基于内生演化和外部联系的多尺度一多主体的新兴产业发展分析框架,并聚焦珠江三角洲工业机器人产业兴起的现象,探究工业机器人产业兴起的过程和影响机制。研究发现:东莞市本地产业基础与工业机器人产业有较强的技术关联性,本地企业采取多样化发展策略和通过企业衍生实现工业机器人企业的出现与集聚。佛山市顺德区依靠与工业机器人强国德国的联系,引入以库卡为代表的国内外领军企业以及德国的工业技术服务体系,带动工业机器人产业发展。珠江三角洲工业机器人产业的兴起同时存在着依托本地产业基础的内生演化和借助外部联系创造新发展路径的两种过程。动态变化的制度环境是促进工业机器人产业兴起的重要因素。这两种过程所需要的制度环境也存在差异,前者更注重培育适宜本地企业演化的产业环境,后者更注重打造利于吸引外部资源的制度环境。
月
年
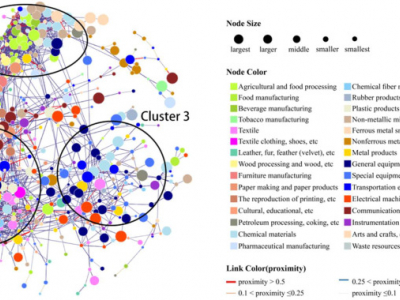
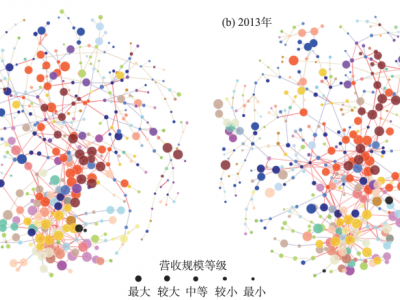
金融危机背景下珠三角产业演化模式及机制研究 ——基于行业空间网络的视角
2008年金融危机对全球制造业尤其是“世界加工厂”珠三角地区的产业链生态空间产生了较大影响,高质量的市场需求、弹性生产模式等冲击了珠三角传统生产模式。大规模生产企业的倒闭,影响了珠三角地区产业集群之间的联系。论文基于演化经济地理学下的复杂网络视角,利用2008年全国第二次经济普查与2013年全国第三次经济普查数据库,在镇街空间尺度上科学构建了广东省制造业行业空间网络,对珠三角5大主导行业组团的内外联系进行了分析,并探讨了珠三角地区镇街尺度上产业空间演化模式,最后以佛山市北滘镇为案例进行了实证。研究发现,珠三角在行业空间网络上体现为主导行业组团内部产业关联度增加、主导行业组团之间的产业关联度降低,反映出为增强地区韧性、适应全球市场的新需求,地区开始跳出本地配套支撑,融入外部生产市场,从相对初级、多元化的分散化发展演化为高端、专业化的集中式发展的产业空间生态模式。未来,珠三角亟需转型,为更快速响应全球市场,建议地区不止于为发达国家提供加工制造,应做强本地特色化的生产品牌,构建本地的完整产业链条,以谋求可持续化的产业发展。
月
年
Transition from factor-driven to innovation-driven urbanization in China: A study of manufacturing industry automation in Dongguan City
Following the reform and opening up of China, the Pearl River Delta (PRD) region became a center of foreign investment due to its comparative advantages of cheap labor costs and low land use prices. The tide of migrant workers, comprising a large surplus rural labor force that flooded into the PRD region, caused a rapid increase in the urban population. From the 1980s to the 2000s, migrant workers were a key force that drove urbanization in China. The utilization of automation technology in…
月
年
2000—2011年产品空间网络视角下中国出口演化及其机制
经济全球化下,研究中国出口演化对经济发展的影响至关重要。西方演化经济学界“产品空间网络”理论的提出,为地区产业发展提供了科学复杂网络方法的新视角。国内学界基于该理论在全球尺度下研究中国产业演化的研究甚为匮乏。文章利用2000—2011年全球海关贸易数据库,以R软件可视化全球动态产品空间,构建了“核心区位度”新指标来科学测度国家在全球贸易格局中的位置,探讨国家在产品空间网络中“核心-外围”位置对本国经济的影响。研究发现,不同发展程度的国家在产品网络空间的位置存在差别,国家的经济表现越好,国家越倾向于在产品空间网络处于核心位置。中国已改变传统上的专业化生产两极分化出口贸易模式,形成相对均衡化的贸易格局,出口优势产品开始从产品空间网络的外围轻工业集群,走向核心地带的机械设备集群及化工综合集群,成为全球网络核心区位度提升幅度最大的国家之一。通过回归模型得出,影响中国在产业空间网络中核心位置演化的主要因素是教育质量与研发投资等因素,而外商投资并未对中国走向网络核心位置存在显著影响。
月
年
China's Export Evolution in Global Product Spatial Network from 2000 to 2011
China’s massive export trajectory can enlighten many developing countries regarding foreign trade. Based on the ‘product space’ theory, the present study analyses the evolution of China’s export economy from three perspectives: (1) comparative advantage from a longitudinal perspective, (2) diversification from a horizontal perspective, and (3) location in dynamic global product space from a spatial perspective. Results show that China’s export economy is becoming more diversified and has…
月
年
经济韧性视角下城镇产业演化的路径依赖与路径创造——基于东莞市樟木头、常平镇的对比分析
在经济韧性视角下,本文基于路径依赖与路径创造理论构建了一个研究城镇产业衰落与转型的分析框架,进而对东莞市樟木头与常平的产业发展路径进行详细梳理和对比分析,探讨地理区位、产业结构等初始条件相似的城镇受到相同外部冲击时出现韧性差异的原因,包括地方制度、技术变革、经济结构、劳动力结构、社会文化氛围等。据此提出转型升级对策:寻找新主导产业,提升经济主体潜力与联系;科学规划空间结构,调整存量用地功能,提高土地利用效率,全面升级硬件设施;重塑强调风险管控与危机意识的社会文化氛围。通过建立演化经济地理学与经济韧性相结合的实证研究范式,本文为产业结构单一城镇提供了具有借鉴意义的韧性增强途径和路径创造方式。
月
年
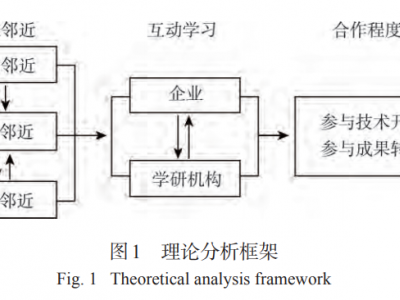
多维邻近性对产学研合作创新的影响--广州市高新技术企业的案例分析
多维邻近性是研究产学研合作创新影响因素的恰当的分析视角.构建“多维邻近→互动学习→合作程度”理论分析框架,运用多案例方法研究多维邻近性对项目形式的产学研合作创新的影响.研究表明:①地理邻近、认知邻近、社会邻近对产学研合作程度的提升均有积极影响,但在技术创新的不同阶段存在差异.②互动学习对多维邻近与产学研合作程度具有显著的调节作用,在内容、方式、强度上有明显的阶段性特征.③地理邻近、认知邻近、社会邻近对产学研合作程度的交互影响呈互补效应或替代效应,在特定情况下存在阶段性差异;互补效应的积极影响通常优于替代效应.