区域经济
月
年
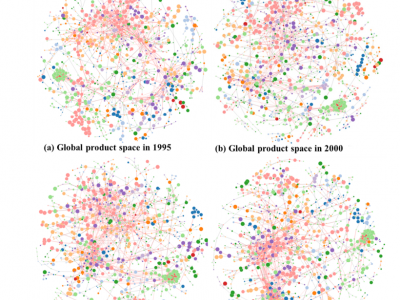
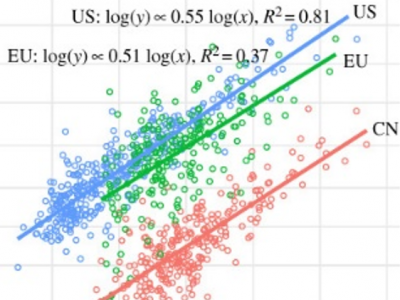
The Spatial and Mechanism Difference in the Export Evolution of Product Space in Global Countries
This study focuses on investigating the changing export patterns, evolution characteristics, and influencing trade mechanisms of countries on a global scale. Based on comprehensive customs data, our study found that core location and export types, including machinery and chemical products, both play positive roles in promoting countries' economic development. Developed countries are more likely to be at the core of the product space and to export machinery and chemical products.
月
年
The patterns and driving forces of uneven regional growth in ASEAN countries: A tale of two Thailands' path toward regional coordinated development
Uneven development has long been a critical issue in geography and urban studies, leading to economically inefficient urbanization, environmentally unbalanced regions, and socially unequal livelihoods. As one result, primate cities and urban primacy form within a hierarchical urban system, to which urban and regional planning must positively respond. It is worth noting that Thailand has experienced a number of important urbanization issues related to developing countries, such as…
月
年
Does Institutional Embeddedness Promote Regional Enterprises’ Migration? An Empirical Analysis Based on the “Double Transfer” Strategy in Guangdong, China
Against the background of globalization, institutional embeddedness has become an important theoretical tool to understand the changes in regional economic patterns. This paper starts by discussing the theory of location choice of enterprises and then uses the statistical method of negative binomial regression to analyze the impact factors of enterprises’ transfer from the perspective of institutional embeddedness by taking Guangdong Province, China, as a case study area. It was found that…
月
年
The inverted U-shaped effect of urban hotspots spatial compactness on urban economic growth
The compact city, as a sustainable concept, is intended to augment the efficiency of urban function. However, previous studies have concentrated more on morphology than on structure. The present study focuses on urban structural elements, i.e. urban hotspots consisting of high-density and high-intensity socioeconomic zones, and explores the economic performance associated with their spatial structure. We use night-time luminosity data and the Loubar method to identify and extract the hotspot…
月
年
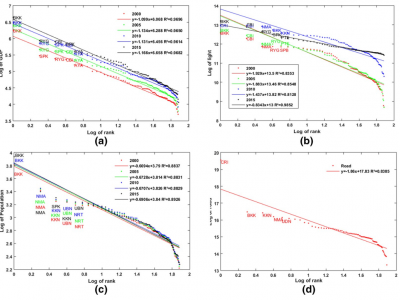
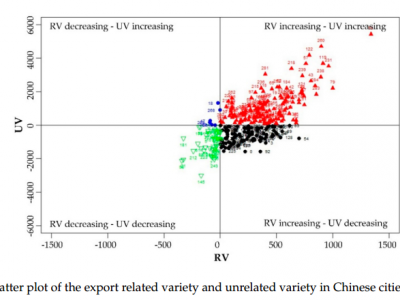
Which Export Variety Matters for Urban Economic Growth, Related or Unrelated Variety?
The relationship between export variety and economic growth has been paid much attention in academia. This paper discusses more deeply the relationship between export related and unrelated variety and economic growth, rather than mere export variety. This paper uses the entropy measurement method to measure the level of export variety of Chinese cities and use the concept of “proximity” proposed by Hidalgo to divide the related variety and unrelated variety. Using the panel data of 252…
月
年
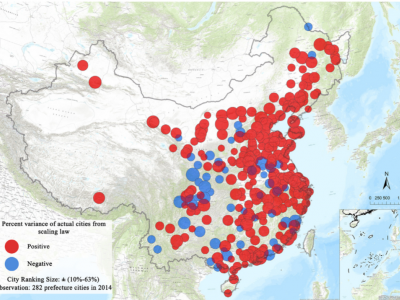
Reinvestigating China’s urbanization through the lens of allometric scaling
Cities are complex systems; we expect the dynamics of the urbanization process to follow the power law, which alludes to the scaling properties of allometry. Urban scaling as a fundamental theory has drawn abundant attention in geography and urban studies literature over the past few decades; yet, there is uncertainty about its applicability in a global context, especially in a fast-transforming urban environment such as China. More importantly, there have been very few studies on the…
月
年
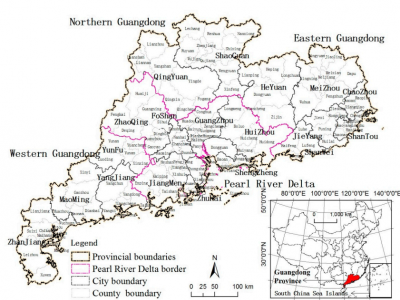
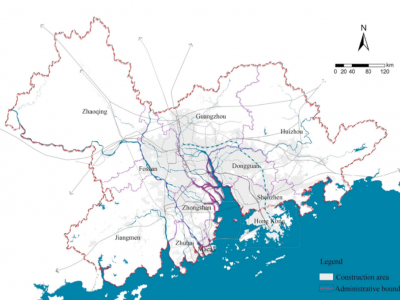
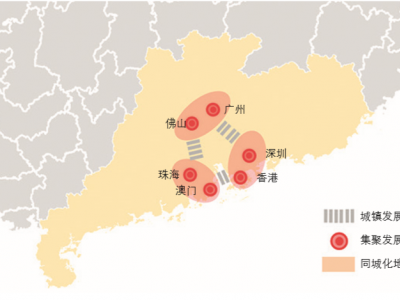
Deciphering the spatial structure of China's megacity region: A new bay area—The Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area in the making
In 2015, the China State Council in its 13th Five-Year Plan for Economic and Social Development strategically initiated the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macau Greater Bay Area, with emphasis on strengthening its role in economic development and its powerful synergy with the all-important The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) in the country and globally. The Greater Bay Area is a unique mega city region situated at the Pearl River Delta, covering the 11 [9 mainland cities +2 special administrative regions (…
月
年
人口集聚对中国城市经济增长的影响分析
人口集聚是新经济地理学关注的焦点,由于连续年份城市建设用地数据难以获取等原因,目前仍无法明确人口集聚是否促进了中国城市经济增长。采用消除连续年份时空异质性的DMSP/OLS夜间灯光数据方法所提取的建设用地等数据,通过构建人口密度影响地均收入水平的理论模型,分析2005-2013年间人口集聚对中国35个大城市经济增长的影响。研究发现人口集聚对中国城市经济增长产生显著的正向影响,其影响程度沿东、中、西部依次递减;在解释机制上,人口集聚主要通过知识和人力资本促进中国城市经济的增长,而知识密集行业占比和高校师生比的空间分布及两者对城市收入的影响是沿东、中、西部依次递减的,是解释人口集聚促进城市经济增长存在空间差异的主要原因。
月
年
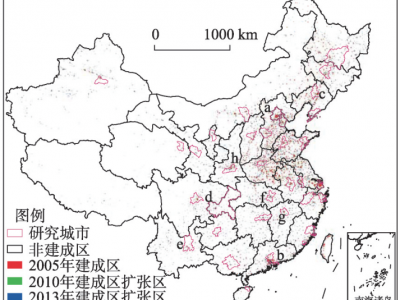
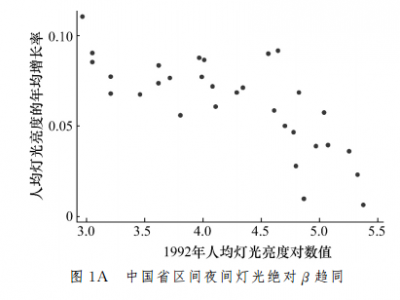
中国地区经济差距动态趋势重估—基于卫星灯光数据的考察
本文采用美国国家海洋和大气管理局公开的全球夜间灯光亮度数据,重新评估中国地区经济差距动态趋势。基于增长理论的趋同分析框架,实证发现,在1992—2012年间,中国无论是在省层面还是在地级城市层面,初始夜间灯光亮度较低的地区,随后都呈现出更快的夜间灯光亮度增长。这一变化趋势与人均 GDP 的变化趋势不完全一致。本文进一步发现,夜间灯光亮度与电力消费密集型的经济活动密切相关,在行政空间维度上呈现出显著的互动追赶特征。
月
年
改革开放以来粤港澳经济关系的回顾与展望
改革开放近40年的发展见证了粤港澳经济合作举世瞩目的成就.粤港澳三地的经济关系由早期单一的“前店后厂”跨地域分工模式向“厂店结合”等多种模式并举演变,实现了地域范围的延展与合作内涵的丰富.进入21世纪后,香港经济转型的同时面临广东省服务业崛起的挑战,粤港澳三地通过基础设施的对接与优化不断争夺腹地,以突破土地资源的束缚实现经济发展空间的拓展;“一带一路”与“人民币国际化”战略背景之下,金融业合作可能成为粤港澳经济合作第三阶段的发展重点.在经济关系转变的同时,粤港澳的空间格局亦由“小集聚、大分散”逐步转向“小分散、大集聚”.分析粤港澳未来经济关系的走向,认为粤港澳区域合作将从分散发展走向边界突破,从宜居湾区走向世界级湾区,从中心-腹地走向枢纽-网络,最终实现对经济关系转变的空间回应.