其他研究
月
年
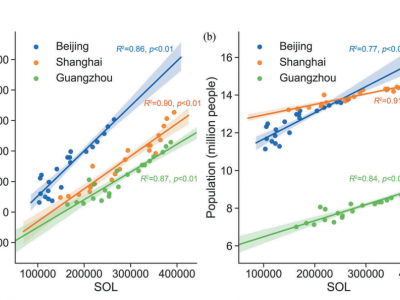
Automation impacts on China’s polarized job market
When facing automation threats, a large Chinese city worker might not be as lucky as a worker in a large US city. Empirical studies found that large US cities exhibit resilience to automation impacts because of the increased occupational and skill specialization. However, in this study, we observe polarized responses in large Chinese cities to automation impacts. The polarization might be attributed to the elaborate master planning of the central government. Cities are assigned with different…
月
年
Measuring cognitive proximity using semantic analysis: A case study of China’s ICT industry
Quantification of knowledge technologies has long posed a challenge to the measurement of cognitive proximity. This paper proposes a method to measure cognitive proximity by mining patent description text with the LDA topic model.
月
年
Symmetry Analysis of Oriental Polygonal Pagodas Using 3D Point Clouds for Cultural Heritage
Ancient pagodas are usually parts of hot tourist spots in many oriental countries due to their unique historical backgrounds. They are usually polygonal structures comprised by multiple floors, which are separated by eaves. In this paper, we propose a new method to investigate both the rotational and reflectional symmetry of such polygonal pagodas through developing novel geometric models to fit to the 3D point clouds obtained from photogrammetric reconstruction.
月
年
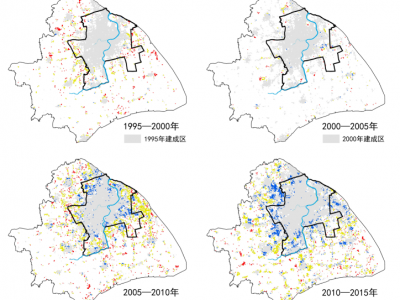
紧凑城市视角下的建成区时空演变特征及其影响因素分析——以上海为例
新时期我国国土空间规划战略的重要任务之一是实现土地资源最佳使用与紧凑城市发展战略,实现新型城镇化的高质量发展。紧凑城市作为国土空间规划的重要策略,对于解决中国快速城市化过程中城市蔓延带来的交通拥堵、资源浪费等城市问题具有重大意义。通过上海市1995—2015年建成区的时空分析,挖掘建成区扩展演变规律。基于重力模型建立紧凑度指标对城市扩展过程进行量化分析,剖析紧凑度的时空演变规律:一是上海市建成区紧凑度先降低后升高,主城区紧凑度高于郊区;二是上海市主城区和郊区紧凑度变化受人口、产业、交通等多种因素的影响。在面向国土空间规划时,提出紧凑城市发展策略及规划响应。
月
年
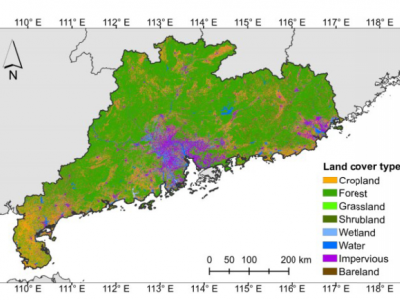
Improved mapping results of 10 m resolution land cover classification in Guangdong, China using multisource remote sensing data with google Earth engine
Land cover information depicting the complex interactions between human activities and surface change is critically essential for nature conservation, social management, and sustainable development. Recent advances have shown great potentials of remote sensing data in generating high-resolution land cover maps, but it remains unclear how different models, data sources, and inclusive features affect the classification results, which hinders its applications in regional studies requiring more…
月
年
Understanding livable dense urban form for social activities in transit-oriented development through human-scale measurements
Transit-oriented development (TOD) has been one of the critical concerns for developing dense urban form.Capturing the human-scaled effects of dense urban form in TOD remains poorly explored. This study aims to devise human-scaled measurements to investigate the areas around metro stations in TOD, focusing on the interaction between the physical environment and residents’ activities. We employed Urban Network Analysis (UNA) in GIS at the building level with fve metrics—Reach, Betweenness,…
月
年
A novel cross-sensor calibration method to generate a consistent night-time lights time series dataset
Night-time lights (NTLs) collected from the Defense Meteorological Satellite Program‘s Operational Linescan System (DMSP-OLS) and the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) of the Suomi National Polar Partnership satellite have been widely used in multiple disciplines. However, the defects of DMSP and VIIRS data itself, and the inconsistency between them, hinder their applications in long-term finer studies. Despite some effective efforts, existing relevant researches are still…
月
年
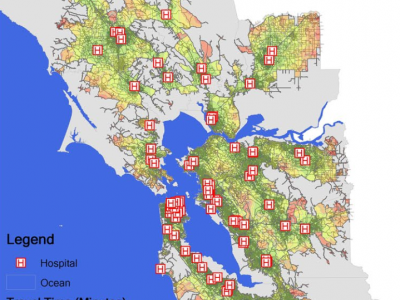
Environment resilience and public health: Assessing healthcare's vulnerability to climate change in the San Francisco Bay Area
This study investigated the vulnerability of people's health to the impact of climate change on healthcare accessibility in the San Francisco Bay Area. The study developed spatial analysis models in ArcGIS with a high‐resolution elevation data set (1 m raster base map) and summarized the scenario assessments of the associations between healthcare and the populations vulnerable to the effects of climate change. The results reveal that 34.3% of low‐income households could reach hospitals in the…
月
年
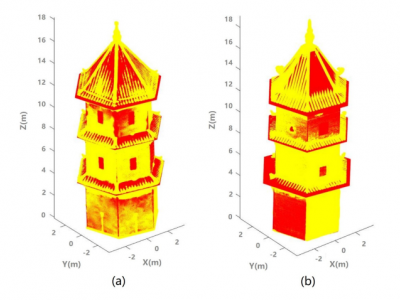
CENTRAL AXIS ESTIMATION FOR ANCIENT CHINESE PAGODAS BASED ON GEOMETRIC MODELLING AND UAV-BASED PHOTOGRAMMETRY
Pagodas are common historical structures in China and some other Asian countries. Symmetries of the pagodas play an important role on cultural and structural aspects. In this paper, we proposed a method estimating the central axis of a typical ancient pagoda in China for examination of its symmetry. We developed a novel geometric model to fit to the point cloud of the pagoda obtained from photogrammetric reconstruction based on UAV imagery. More specifically, we developed a novel geometric…
月
年
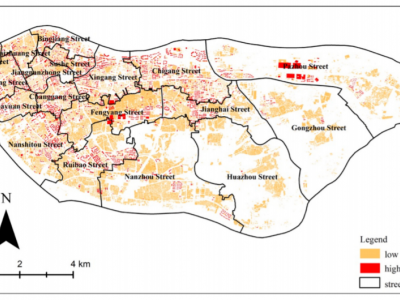
Exploring the Quality of Urban Green Spaces Based on Urban Neighborhood Green Index—A Case Study of Guangzhou City
Urban green space (UGS), as a form of green infrastructure, has been given increasing attention in urban planning and its policies. The quality of a UGS is fundamental for the sustainable development of the urban economy, society, environment, and quality of human life, although UGS is unevenly distributed within cities. Aiming to analyze the quality of UGS at the scale of Jiedaos in China, this paper took Haizhu district in Guangzhou as a case study based on collected data from 2010 and aerial…